Abstract
TL;DR: Stable Diffusion can be improved via learning from human preferences. The trained model is better aligned
with user intentions, and also produce images with less artifacts, such as weird limbs and faces.
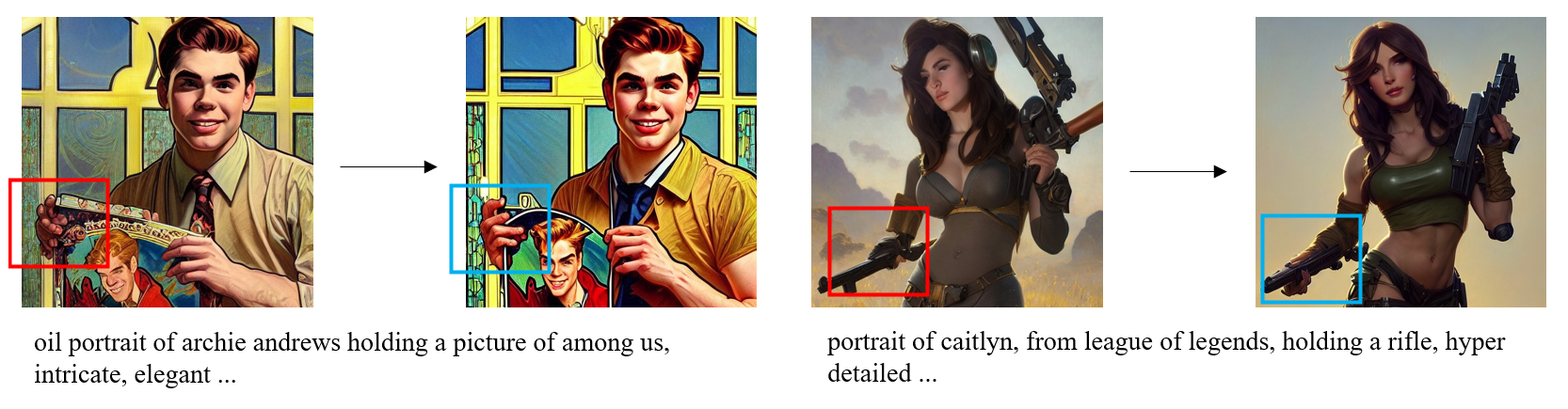

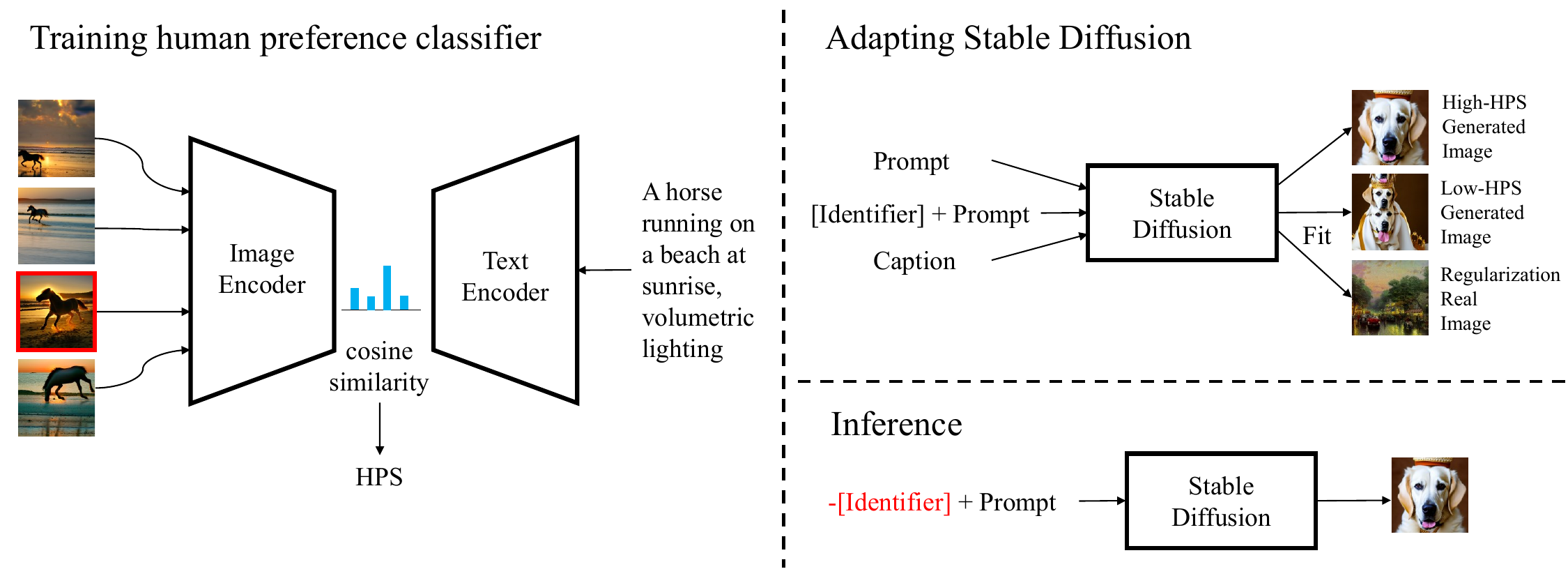
Recent years have witnessed a rapid growth of deep generative models, with text-to-image models gaining significant attention from the public. However, existing models often generate images that do not align well with human aesthetic preferences, such as awkward combinations of limbs and facial expressions. To address this issue, we collect a dataset of human choices on generated images from the Stable Foundation Discord channel. Our experiments demonstrate that current evaluation metrics for generative models do not correlate well with human choices. Thus, we train a human preference classifier with the collected dataset and derive a Human Preference Score (HPS) based on the classifier. Using the HPS, we propose a simple yet effective method to adapt Stable Diffusion to better align with human aesthetic preferences. Our experiments show that the HPS outperforms CLIP in predicting human choices and has good generalization capability towards images generated from other models. By tuning Stable Diffusion with the guidance of the HPS, the adapted model is able to generate images that are more preferred by human users.